Wholistic Therapies
News

What's News: (See the stories below)
A Golfing Success Story
An Update on Autism
Success Story
Frances Bondad Pro Golfer
http://www.dailytelegraph.com.au/sport/golf/tapping-into-talent/story-e6frey60-1226253822605
A Golfing Success Story
An Update on Autism
Success Story
Frances Bondad Pro Golfer
http://www.dailytelegraph.com.au/sport/golf/tapping-into-talent/story-e6frey60-1226253822605
Autism Update
Autistic Spectrum Disorders (ASD) are a series of Neuro-developmental disorders characterised by repetitive behaviours, social withdrawal and communication deficits. People with ASD display a wide range of cognitive ability, ranging from mental retardation in children to high functioning adults with an above average IQ.
There are three main categories of ASD:
1. Autistic disorder – The diagnosis of autistic disorder is given to individuals with significant impairment in social interaction and communication, as well as restricted and repetitive focused activities. Behaviours are generally evident prior to three years of age. There are several subtypes of autism:
a. Regressive Autism: Is when a child appears to develop normally but then starts to lose speech and social skills, generally between the ages of 15 and 30 months.
b. Infantile Autism: This occurs when children do not achieve developmental milestones and are usually determined as having had autism from infancy.
2. Asperger’s disorder – Individuals with Asperger’s have difficulties with social interaction and social communication as well as restricted and repetitive activities and behaviours. However, those with Asperger’s do not have a significant delay in early language acquisition, cognitive abilities or self-reliance skills. The condition is often detected later than autism as speech usually develops at the expected age.
3. Pervasive Developmental Disorder – (PDD)
Diagnosis is made when an individual has marked social impairment but does not meet the full criteria for either autistic or Asperger’s disorder. These individuals may also have some impaired communication skills and/or restricted or repetitive activities, interests and behaviours.
The diagnosis of ASD is based solely on a particular developmental pattern in the child and is historically considered as a psychiatric disorder. Whilst a diagnosis is made on observation, there are no quantitative biochemical tests to confirm diagnosis. There is however evidence that indicates numerous biochemical abnormalities in these children, including oxidative stress, decreased methylation capacity, mitochondrial dysfunction, heavy metal accumulation, intestinal dysbiosis, inflammatory bowel disease, immune deregulation and cerebral hypo fusion.
Aetiology / Risk factors
Some aetiology and risk factor possibilities include:
Inherited genetic polymorphisms influencing detoxification (methylation) and dopamine signalling.
Gender bias, with a 4:1 ratio (males to females)
Heavy metal exposure – especially mercury, but others may be also implicated.
Immune dysfunction – Severe maternal inflammation, infections, allergy and autoimmune response during pregnancy may lead to a flood of cytokines causing microglial activation, leading to a CNS inflammation, thus interfering with neurodevelopment.
Immune dysfunction – Mild, acute or chronic gut mucosal inflammation associated with ileo-colonic lymphoid nodular hyperplasia (LNH) leading to “autistic colitis” may be a cause or perhaps a consequence of systemic oxidative stress and inflammation associated with autism.
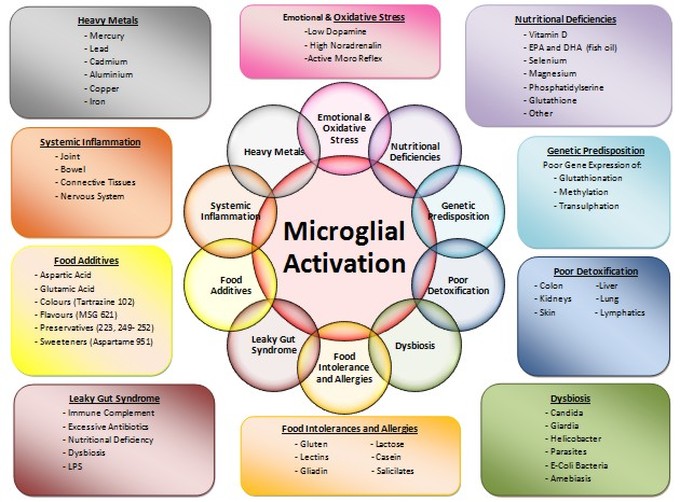
After reviewing the latest research into Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD), Dr. Adam Nichols formulated a new and extensive protocol for treating Autism that addresses the multi-faceted components of ASD. He believes the key to the disorders is primarily the Microglial Activation (MGA) leading to brain inflammation. The Microglia is the Central Nervous Systems’ immune system and when over activated responds like an autoimmune disease, causing disruption, damage and chemical imbalance to the brains’ tissues. The Protocol is aimed at addressing the 10 major components that could cause the excited immune response of MGA. He has now developed a specific Osteopathic therapy to reset or switch off an overactive MGA.
These components are:
1.Endo-toxins & Oxidative Stress
2.Heavy Metal Toxicity
3.Systemic Inflammation
4.Chemical Sensitivity from food additives
5.Leaky Gut Syndrome
6.Food Intolerances and Allergies
7.Dysbiosis
8.Poor Liver Detoxification
9.Nutritional Deficiencies
10.Genetic Predisposition
The program is presently in its early stage of proving efficacy.
